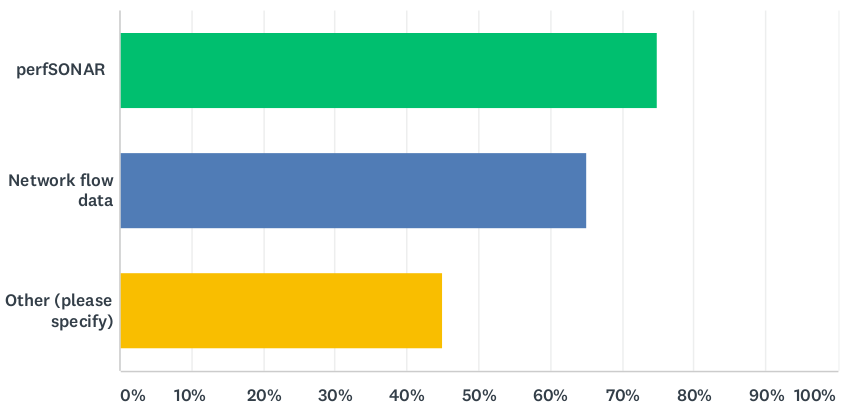
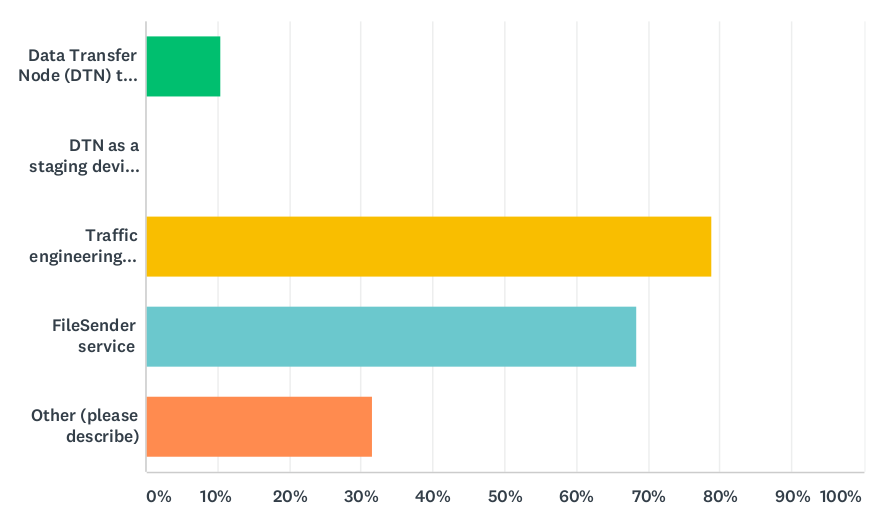
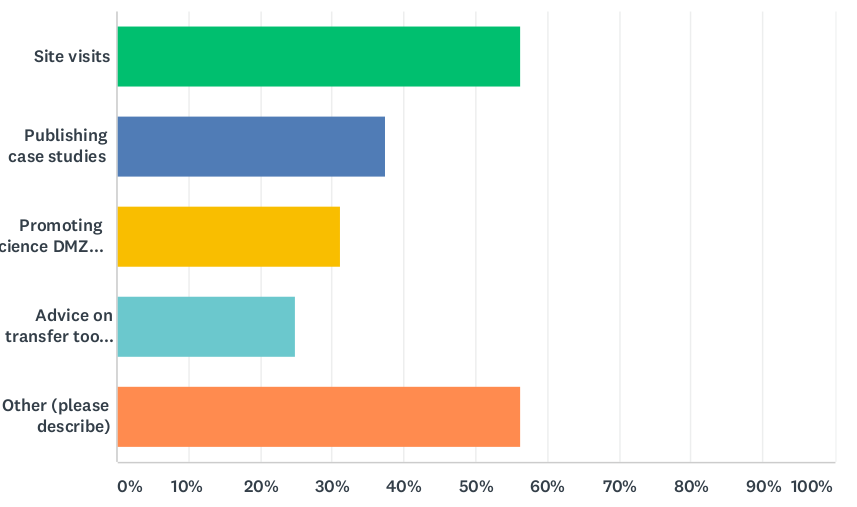
WP6 (formerly T1, now T2) is currently investigating how European NRENs support their user communities in making optimal use of their networks for large scale data transfers, including the use of Data Transfer Nodes (DTNs).
It would be very useful for us to get your feedback regarding your current practices and your interest to engage further with WP6 T1 on this topic (gn4-3-wp6-t1-dtn@lists.geant.org). Your feedback will be taken in consideration to redirect our future work.
GÉANT NREN Survey results
Survey presentation:
- STF meeting, 22-23 Oct. 2019, Copenhagen (.pdf)
Questions:
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
•
prpucsd.edu
Q2. Are
eVLBI Q3. What
a
Q4. WhichQ5. What
Q6. Do