Introduction
WaTTS (the INDIGO Token Translation Service) is a plugin-based Token Translation Service. Enabled by plugins, several credentials (e.g. SSH keys, X.509, S3 access tokens, etc.) are supported. WaTTS accepts many different implementations of OIDC providers (EGI-CheckIn, B2Access, Human Brain, Google and Indigo IAM)
In this pilot, we have implemented a plugin to demonstrate the integration with the RCauth.eu online CA. The WaTTS plugin implements a MasterPortal and VO-Portal for the RCauth CA. After authenticating in WaTTS with any OIDC Provider, a certificate may be requested. For this, the user is redirected to the RCauth CA WAYF. There, she may choose which home-IdP to use for authenticating to RCauth. In this autentication step, the LoA must be high enough to fulfill policy requirements. To date B2Access, Checkin and a set of individual IdPs support these requirements.
NOTE:
In the first version of this pilot, we will use the development instance of RCauth, which does not use a WAYF but redirects users directly to the EGI-AAI-Dev instance.
Upon successful authentication at RCauth.eu, the users browser is redirected back to WaTTS, where he is given a proxy of his certificate. The full certificate is stored inside a myProxy. Development to provide a VOMS proxy is on-going.
Detailed description
Goal of the pilot is to demonstrate how the credentials can be managed according to user's identity. From the research/user point of view, the desired behavior is having an SSH access to desired VMs. From the administrator/coordinator point of view, the desired outcome is providing access to users in a straightforward manner, as easy as user uploading it's SSH key. However, such access should be granted only to authorized users. Therefore, LoA discrimination is used.
Pilot example is following:
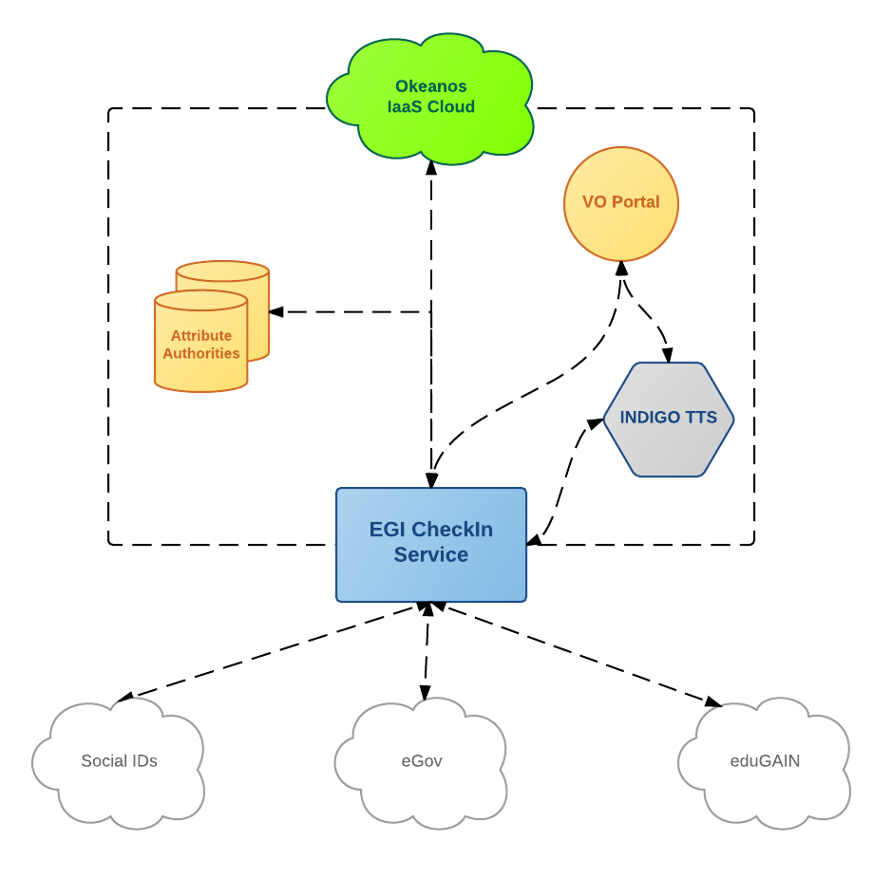
- Community has reserved resources on the ~okeanos IaaS cloud through EGI
- Users authenticate to their home organizations using the EGI CheckIn Service
- WaTTS INDIGO TTS is deployed at KIT, and is used to manage/upload SSH keys
The pilot structure is shown in picture below.
The pilot authentication flow is shown below:
- User access the WaTTS page, and selects the desired OIDC provider, in this case EGI CheckIn Service
- User is redirected to the desired OIDC provider. In case of EGI CheckIn Service, user can select between his home IdP, or social networks (SN) (Google, etc.), among others. However, these do affect the LoA granted to the user, i.e. home organisation has Substantial LoA, while SNs have Low.
- User is prompted to accept the release of information, and at the end, the information about the user is returned to the WATTS (i.e. LoA, issuer, name, mail, etc.)
- User then selects the desired action.
- User uploads/generates an SSH key
- SSH key is deployed to the desired VMs, and username and hostname is shown to the user.
It is important to mention that at neither step the credentials (in this case SSH keys) are stored on WATTS service.
WaTTS is still in development, however, it is also in production. As already mentioned, it is not limited to EGI OIDC providers, but already supports Human Brain Project (HBP), b2access, Google, and naturally, INDIGO IAM (INDIGO Access Management). Adding additional IdPs or configuring the service is straightforward. Support for additional credentials is done through plugins, which can be further developed as needed.
WATTS source and info pages:
https://github.com/indigo-dc/tts
https://www.gitbook.com/book/indigo-dc/token-translation-service
Note that page might be moved in the future, probably to https://github.com/indigo-dc/watts.
| Pilot resources | |||
|---|---|---|---|
WATTS service (https://watts-dev.data.kit.edu) | |||
EGI CheckIn service | |||
2 VMS provided by ~okeanos. | |||
| KIT Grid certificate (used to authenticate with EGI CheckIn service), alternatively Google account is used, however LoA connected with Google account is not sufficient to upload keys (this is by design, it is configurable, naturally) |
Demonstration workflow
| Access to the cloud resources | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Access WaTTS instance at https://watts-dev.data.kit.edu Select "European Grid Infrastructure" and click on "Login".
| |
| 2. | Select your Identity Provider from the discovery page (WAYF). The institutional IdP to select (for this demo) is: IGTF Certificate Proxy, and then we use the institutional grid certificate (in this case, KIT Grid Certificate) | |
| 3. | This page displays which values will be released by IGTF-to-eduGAIN-Proxy. User should click on Yes to accept and proceed.
| |
| 4. | This page displays which values will be released by EGI-CheckIn. User should click on Yes to accept and proceed. We can see that the LoA is now Substantial. | |
| 5. | Upon successful login, the user is redirected to the WaTTS. We then select the desired plugin, in this case aarc_ssh, and we can select either Request, or Advanced. First option creates SSH key par for the user, and deploys the public key to the VMs. User then must download the key pair if intends to use them, since the keys are never stored on WaTTS. If skipping this step, user must recreate the SSH keys again. Second option (Advanced) will enable the user to upload its own public SSH key. | |
| 6. | If user select Advanced option, then it is able to upload its own key. After pasting the key, user should click on the Submit button.
| |
| 7. | After successfully uploading or generating SSH key, the user now has SSH access to VMs. The username and full VM hostname is displayed to the user. | |