InfiniBand is a high-performance network architecture developed by the IBTA (InfiniBand Trade Association). IBTA is a group of 220 or more companies founded in 1999 with the purpose of developing a technology
which would substantially outstrip the capabilities of industry-standard I/O systems.
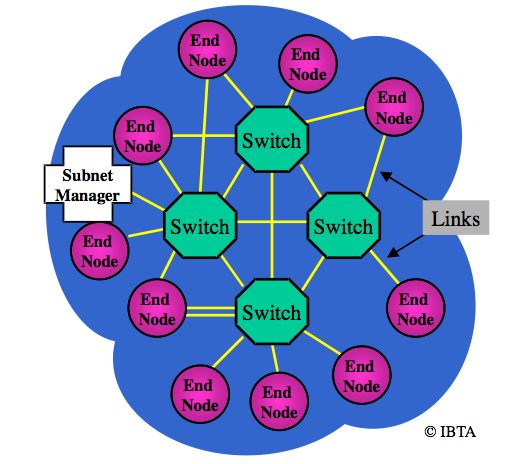
The InfiniBand architecture (IBA) is mainly based on switching fabric and is designed for use in I/O networks, such as storage area networks (SAN) or cluster networks, where low latency plays an extremely important role.
A large IBA network is composed by different subnets joined together by routers.
The elements of a subnet are endnodes, switches, links, and a subnet manager.

Endnodes exchange messages routed by switches over links. No routing exists in IBA. A subnet discovery is performed in the beginning by the Subnet Manager.
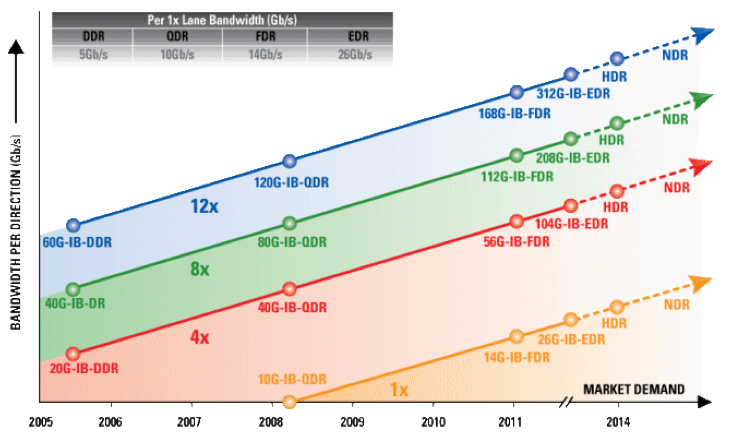
IBA offers point-to-point bidirectional links with five different signaling data rates:
In IBA, QoS is supported through Virtual Lanes (VL) which also provide a mechanism to avoid Head of Line (HoL) blocking . VLs are separate logical communication links which share a single
physical link. As a packet traverses the subnet, a Service Level (SL) is defined to ensure its QoS level. Each link along a path can have a different VL, and the SL provides each link a desired priority of communication.
Each switch/router has a SL to VL mapping table that is set by the subnet
manager to keep the proper priority with the number of VLs supported on each link.
Therefore, the InfiniBand Architecture can ensure end-to-end QoS through switches, routers and over the long haul.
– Main.AlessandraScicchitano - 03 May 2012