Architecture Overview
The architecture of the testbed is based on the use of self-containing containers (Docker) for the software products (IdP, SP, Proxy). These containers are maintained by a product maintainer and made available at a location of their choice (e.g. Docker Hub). The key component of the testbed is a centrally managed repository (GitHub) that contains the configurations of all products, i.e. deployment and test instructions. A user only has to clone the central repository and can then select the required software products and have it deployed in a target environment (e.g. local or cloud). In addition, the testbed provides a way to run automated web-based tests using Selenium, which are tailored to the selected software products.
This approach makes the administration of the testbed very lightweight and gives developers and other maintainers the opportunity to make their own products easily available.

Roles
Product Maintainer
Testbed Administrator
Testbed User
Activities
[01] package product
[02] provide config
[03] accept config
[04] update testbed
[05] fetch config
[06] deploy config
[07] fetch product
[08] manage
Docker Specification
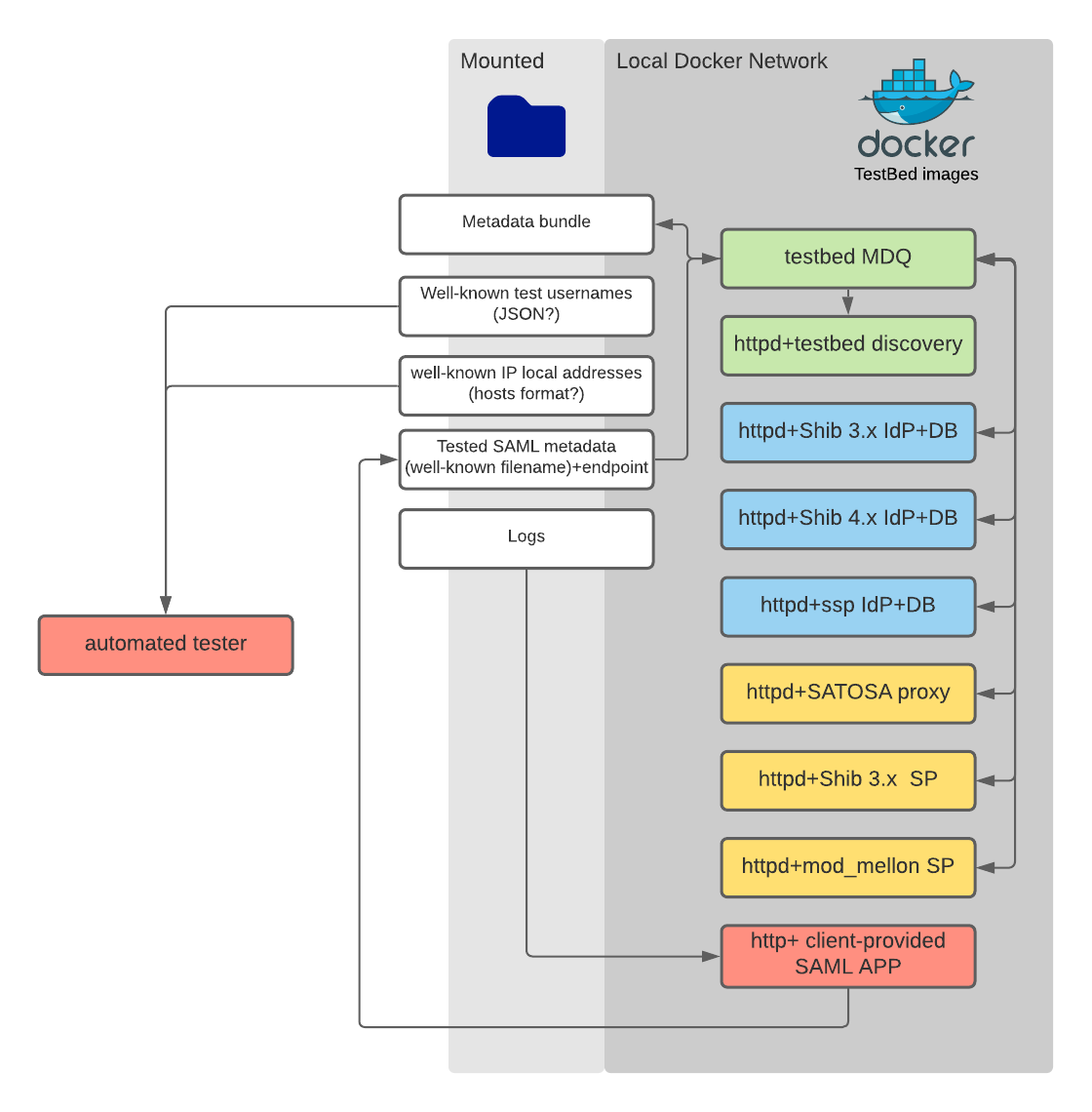
The architecture is based on docker. The SAML software to be tested should be available as self-contained docker images. However, we also need to make sure that they can interfederate with each other.
The requirements of this are the following.
Domain Name Resolution: There needs to be a mechanism for discovering what IP addresses got assigned to individual docker images. The docker images should have a local domain name that should be resolved. The initial proposal is to generate a hosts file and have the docker images use their pre-allocated slots.
Metadata Exchange: each docker image should make its metadata available for download on a pre-arranged endpoint. Furthermore, each docker image should know about the metadata of the other images. Therefore they either need to use a pre-arranged MDX service or they need to have some pre-arranged way for taking up metadata, i.e., via a mounted folder specifically for this purpose
The logs should be made available from outside of the docker images for investigation. For better debugging it is advised that debug mode is used.
Any IdPs should support a pre-arranged set of test users' credentials and released attributes, in order to support automated testing.
Test Automation
The testbed offers the capability to define and execute automated web-based tests using Selenium.

<<test sequence diagram>>