...
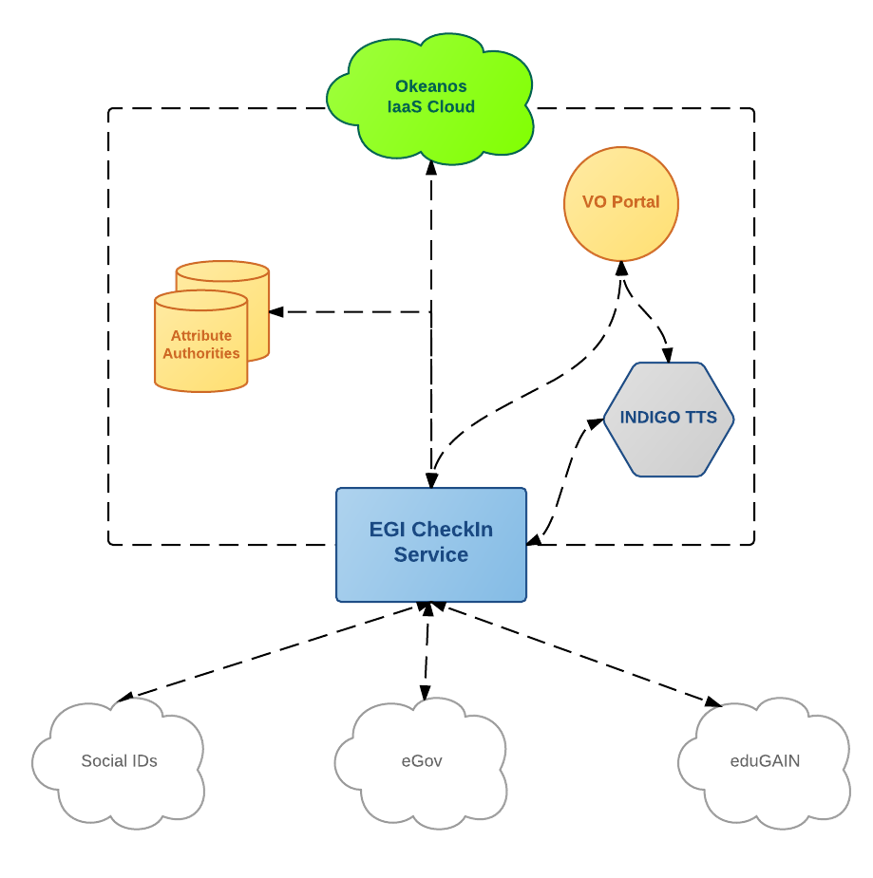
The pilot structure is shown in picture below.
The pilot authentication flow is shown below:
- User access the WaTTS page, and selects the desired OIDC provider, in this case EGI CheckIn Service
- User is redirected to the desired OIDC provider. In case of EGI CheckIn Service, user can select between his home IdP, or social networks (SN) (Google, etc.), among others. However, these do affect the LoA granted to the user, i.e. home organisation has Substantial LoA, while SNs have Low.
- User is prompted to accept the release of information, and at the end, the information about the user is returned to the WATTS (i.e. LoA, issuer, name, mail, etc.)
- User then selects the desired action.
- User uploads/generates an SSH key
- SSH key is deployed to the desired VMs, and username and hostname is shown to the user.
It is important to mention that at neither step the credentials (in this case SSH keys) are stored on WATTS service.
...